Radiopharmaceutical Therapy
Radiopharmaceutical Therapy in Precision Oncology
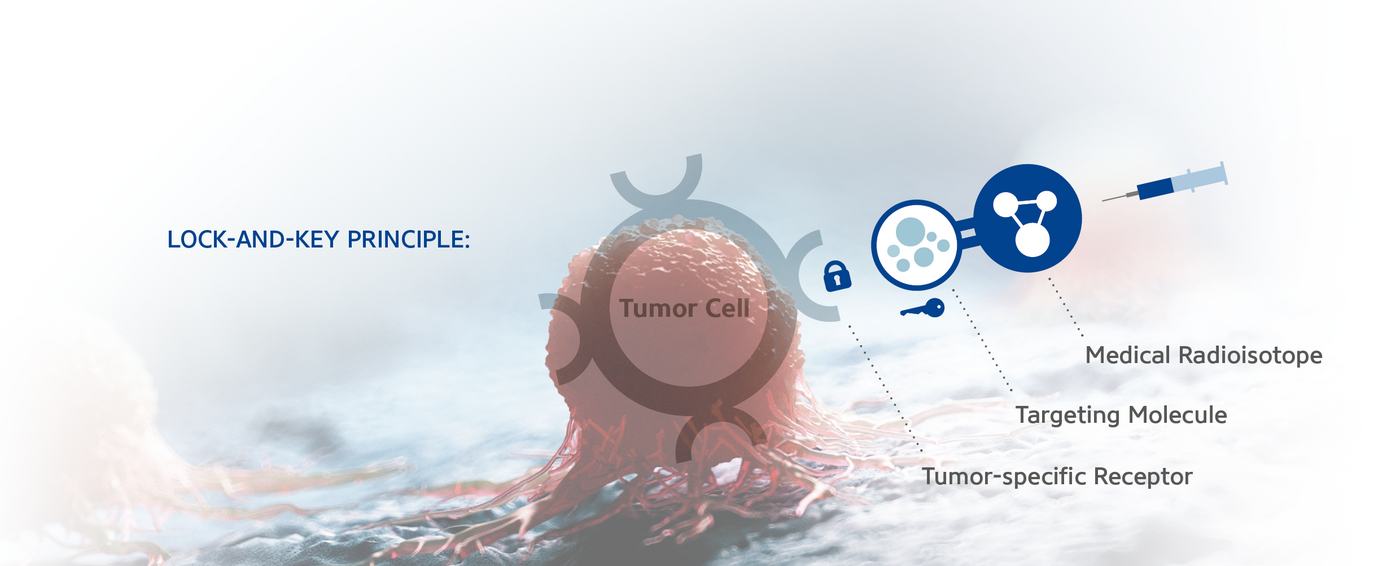
Radiopharmaceutical Therapy (RPT) or Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy (PRRT) is a medical specialty using very small amounts of radioactive compounds, called radiopharmaceuticals, to diagnose and treat various diseases, like cancer. Once injected into the patient, the radiopharmaceutical finds its way to the tumor through the bloodstream and binds to the tumor specific receptor according to a lock and key principle.
Radiopharmaceuticals contain a targeting molecule (e.g. peptide or antibody) and a medical radioisotope, conjugated by a chelating agent. The targeting molecule binds to a tumor specific receptor, according to the lock and key principle. In most cases the targeting molecule can be used for both diagnosis and therapy – only the radioisotope has to be changed. This opens up the way for the application of Theranostics in the field of Precision Oncology.
For diagnostic applications radioisotopes with short half-lives are used. With highly sensitive molecular imaging technologies like PET (Positron Emission Tomography) or SPECT (Single Photon Emission Tomography), pictures of organs and lesions can be created and diseases can therefore be diagnosed in their early stages.
Medical radioisotopes with longer half-lives are applied for treatment. To destroy the tumor, minimal cytotoxic doses of ionizing radiation have to be submitted to the tumor site before decay. A highly precise localization of the toxicity ensures that healthy tissue in the surroundings of the targeted tumor is minimally affected.
Key Facts
- Solid tumors such as neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), osteosarcoma or ovarian cancer can be detected at an early stage by in vivo imaging
- In most cases the targeting molecule can be used in a theranostic approach for diagnostics as well as for therapy
- Highly precise diagnostic and therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals can deal with specific tumors in the most effective manner
- Targeted Radionuclide Therapy as a treatment option where other therapies are limited or even fail
For Healthcare Professionals:
Visit our Theranostics.online learning platform to expand your oncology expertise. The website provides you with a comprehensive introduction to radionuclide therapy and oncology theranostics. The training materials have been developed with leading experts and provide insights into current research and application fields. The platform also features videos, up-to-date information on industry trends, and expert tips from leading nuclear medicine physicians and oncologists to help you make informed decisions in your practice.
